Electricity is a fascinating creation. We rely on this tool for our everyday lives, yet its inner workings are a mystery to most people. Enter the resistor.
Resistors are essential for mundane tools such as electric stoves, microwaves, and data centers. Without them, we’d be experiencing much more unstable technology and wasting electricity. If you need to learn about your equipment’s inner workings, understanding resistors is a fundamental starting point.
Below we’ll explore the resistor, how it works, and what you should know about its applicability in everyday applications.
The Function of Resistance in Electricity
Let’s start with the most apparent aspect of resistors: resistance! This detail is the defining hallmark of resistors, allowing these tools to slot into everyday life.
Before we talk about resistance, we must discuss how electricity works. Electricity can only move through materials thanks to electrons (or tiny charged particles). You risk being electrocuted or starting a fire when you cannot keep such an intense energy source in check.
Related: Buying Ethernet Cables? Here’s What You Need To Know
Conductors vs Insulators
Common knowledge around electricity is that metals are very good conductors. How exactly does this work, anyway?
Metal is a good conductor due to its structure: since they allow some movement of electrons, it can transfer electricity or heat without trouble. Some of the most effective metals for conducting electricity are:
- Silver
- Aluminum
- Copper
Plastic is one of the best-known insulators, holding back a high volume of electrons with no issue. On the other hand, insulators don’t do an excellent job of passing electricity or heat through them. This feature stems from a lack of free movement for electrons to move around.
Building a reliable data center takes time, planning, and the right resources. We’re proud to offer businesses the ability to construct exactly what they need to stay competitive.
Why Do We Need Resistance?
Electricity is involved in just about everything you do. Whether you’re using your phone to send a text or an email online, you rely on this tool to navigate your life.
When electricity is compromised, your entire day comes to a halt.
Resistors allow us to manage how much electricity we use in a single use. For example, ovens use resistors to ensure you only use a certain amount of heat to boil your water. Similarly, a television uses resistors to use specific electricity volumes to brighten the screen or raise the volume.
Without resistors, you run the risk of wasting electricity unnecessarily. Too much electricity may also short-circuit the device, damaging its wires and potentially injuring the user.
Related: Data Center Cleaning Best Practices
How Resistors Work
Now for the main course! Resistors are incredibly helpful in day-to-day life, protecting our investments and physical safety.
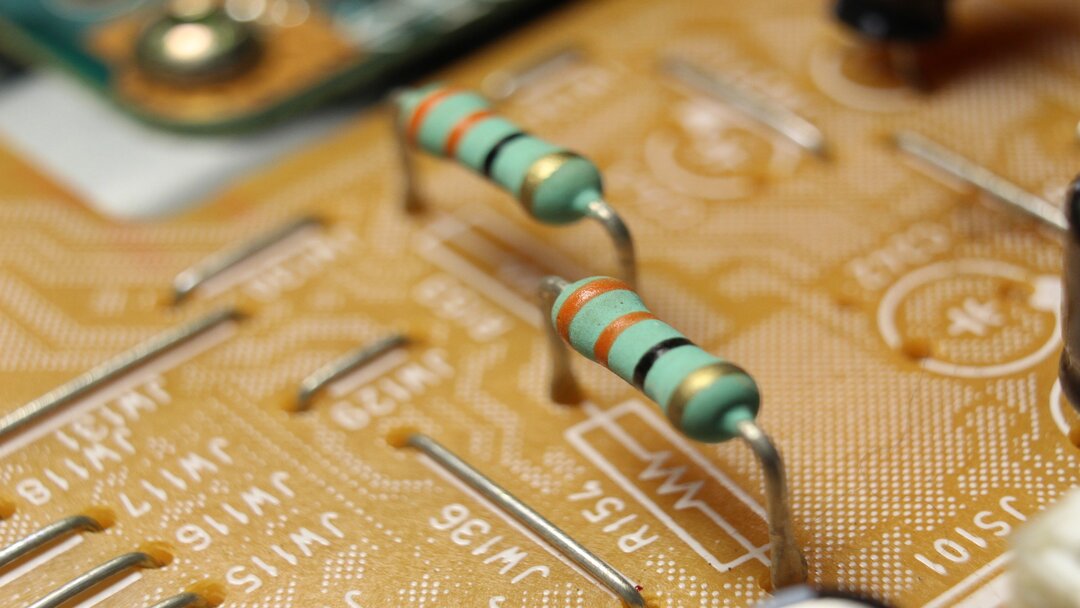
While technology grows at the speed of light, resistors tend to look similar across the board. A resistor resembles a little wooden doorknob (even though it’s not made out of wood). This tool boasts several colored stripes and two connections on either side to hook it into the circuit.
Resistors are designed to regulate and control the flow of electricity through an application. The resistor’s size and the material will affect how well it does its job.
Wire-Wound
Resistors come in two flavors: wire-wound and carbon film. You’ll be able to instantly tell if your resistor is wire-wound if there’s a ceramic rod on the inside with copper wiring.
Copper is an incredibly efficient metal for conducting electricity, which begs the question: why use it inside a resistor? To clarify, the copper on the inside should be very thin and wrapped in a continuous loop. This function ensures electricity is controlled carefully instead of stopped abruptly.
Carbon-Film
Your resistor might also come in the form of a carbon film. These resistors are more affordable but not quite as polished as wire-wound.
Instead of using a thin copper wire to stop electricity gradually, carbon-film resistors use looping spirals of carbon. While carbon is still able to modulate electrical charges, this material lacks fine control and higher temperature stability than copper.
Related: What is Arc Flash? What to Know for Prevention
Why You Need to Choose the Right Resistors
Resistors are a key component of everyday applications. Whether you’re trying to build your own data center or are purchasing a new coffeemaker, we recommend studying this fascinating tool.
The function of a resistor is to control, reduce, or halt the amount of electricity moving through an appliance. They come in two forms depending on the purpose or cost of the item: wire-bound and carbon-film. Wire-bound is more effective at regulating electricity due to copper’s high conductivity, while carbon film is a cost-effective option for simpler applications.
Are you setting up a new data center this year? Contact us today for assistance with electrical engineering, cooling, and more!
Last Updated on June 8, 2023 by Josh Mahan